“Affairs are easier of entrance than of exit, and it is but common prudence to see our way out before we venture in”
(Aesop 620 BC-560 BC).
Projects are an arena that can be fraught with conflict. Disputes and ‘fights’ of all types occur, ranging from $million claims, through many types of negotiation, to personal battles with an adversary. Smart operators do not get into a fight they don’t expect to win but often there is no choice! And whilst seeking a ‘win-win’ outcome is desirable[1], in many situations the only real option it someone wins and someone loses. The art of effective dispute management is to make sure any ‘wins’ are worth the cost and more importantly making sure any losses are manageable – Pyrrhic victories[2] are the route to eventual defeat.
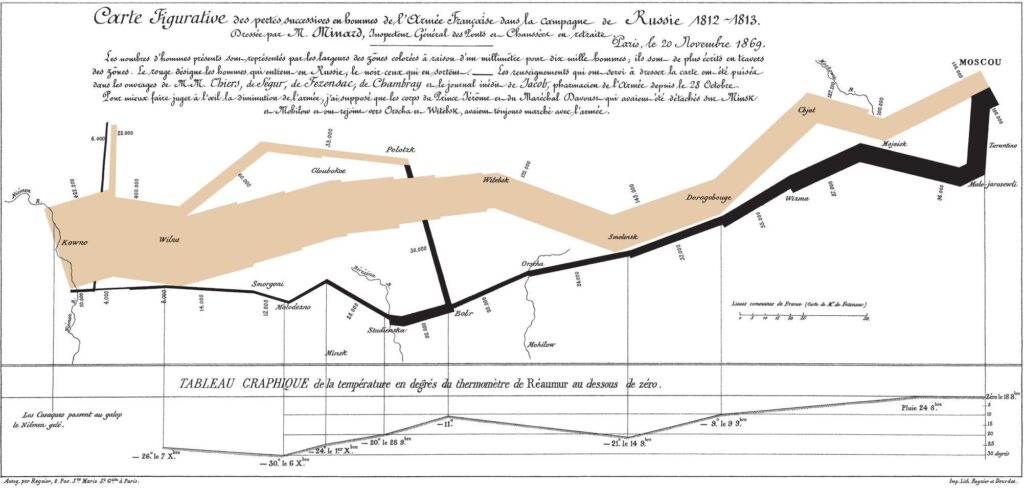
The Napoleonic wars offer some interesting history lessons. Napoleon’s first reign as Emperor was put into terminal decline by the losses suffered by his Grande Armée during the invasion of Russia in 1812 -13. The Grande Armée was a very large force, numbering nearly half a million men from several different nations, probably less than 100,000 left Russia (22,000 from the main army and the remainder from supporting formations and repatriated prisoners).
Grasping the scale of this military and human disaster has always been difficult. Most people are familiar with the horrors suffered on the retreat from Moscow; few people realise over 2/3rds of the French army was killed or died during Napoleon’s ‘successful’ campaign leading to the capture of Moscow.
Charles Joseph Minard, a French civil engineer, drew his famous map (below) to illustrate the losses that Napoleon’s army suffered in the Russian campaign[3].
During Napoleon’s advance, the Russians lost numerous battles but preserved their army and cannon, employed a ‘scorched earth’ policy to starve the invaders (at great cost to the civilian population), evacuated and burned Moscow and maintained a relentless pressure on the French supply lines. Napoleon assumed that once he had captured Moscow, he would automatically ‘win’ the war, the Russians were prepared to ‘lose’ by this definition and accept massive suffering among their civilian population in order to win total victory in the longer run. The Duke of Wellington used similar tactics in the Peninsular wars (Spain / Portugal) retreating to the Lines of Torres Vedras around Lisbon before starting the counter attacks that led to the end of the first Napoleonic Wars.
 Napoleon’s second reign as Emperor ended at the Battle of Waterloo. Waterloo was a catastrophic defeat for the French with no possibility of withdrawing or regrouping. Had Napoleon kept his ‘exit options’ open and been able to withdraw a large part of his army back into Northern France this round of wars would have continued for years and any number of possibilities could have been created. Instead, Napoleon committed his last major reserve late in the afternoon in a final desperate attempt to break the British line before the Prussian army became fully engaged in the battle, the gamble failed and the war was over.
Napoleon’s second reign as Emperor ended at the Battle of Waterloo. Waterloo was a catastrophic defeat for the French with no possibility of withdrawing or regrouping. Had Napoleon kept his ‘exit options’ open and been able to withdraw a large part of his army back into Northern France this round of wars would have continued for years and any number of possibilities could have been created. Instead, Napoleon committed his last major reserve late in the afternoon in a final desperate attempt to break the British line before the Prussian army became fully engaged in the battle, the gamble failed and the war was over.
In contrast, whilst the British army was being pounded by the French (suffering a 25% casualty rate), the Duke of Wellington kept his elite light cavalry in reserve to cover the army if a retreat had became necessary; this is despite having lost his heavy cavalry earlier in the day. The Duke of Wellington was prepared to risk losing a battle to protect his army and fight another day, whereas Napoleon won all of the major battles in Russia and lost the war and then lost everything at Waterloo.
How does this translate into modern project management? There are several important lessons to be learned from history:
- Don’t start a fight without a very clear understanding of the outcome you want and the costs involved. You need a payback in the region of 5 to 1 before the cost of litigation becomes worth considering.
- In negotiation understand your BATNA; BATNA = ‘Best Alternative To a Negotiated Agreement’. If you are pushed to the level of your BATNA, simply walk away.
- It’s nearly impossible to achieve, but try to keep emotions out of your decision making. Non-attachment is a very powerful tool[4].
- Some fights are worth losing! The Russians fought and lost several battles to damage the French army. This is particularly important if your opponent is a powerful bully – if ‘winning’ the fight hurts them enough (and you can lose without too much damage) the effort can be worthwhile.
- Even when you expect to win have a way out planned, you may just need it.
- Take a long-term view; reputations and relationships take a long time to build but can be destroyed in minutes.
- Apply effective risk management and do your sums – there is no point fighting if the cost is more than the likely winnings. Even when there is a surplus – you expect the outcome to be positive, discount your ‘winnings’ by the probability and cost of losing. There are no ‘guaranteed’ outcomes.
When you apply these lessons, if the issue or ‘claim’ not worth fighting over look at the alternatives, if you have a choice, constructive negotiations (win-win) or just walking away are options to consider – all that may be at risk is your ego. If these options are not feasible, plan how to lose for the least cost, whist hurting your aggressor so they think twice about taking you on again in the future.
The other important aspect of losing is dealing with the knowledge you have failed. Failure is inevitable in life, there is only one winner in every sporting contest, court case and dispute, and sometimes no-one wins! The challenge is to make use of failure:
Winston Churchill “Success is stumbling from failure to failure with no loss of enthusiasm”.
Sofia Loren “Mistakes are part of the dues one pays for a full life”. A few thoughts:
- Culture is important, people need to feel safe in admitting mistakes.
- Old failures disappear. As long as you acknowledge failure, it slips away both in your own memory and in the memories of those around you over the course of a few months. Unacknowledged, it tends to fester. Getting it out is the only way to go.
- Failure is, really, no big deal. Failures happen, we acknowledge them, they fade away.
The idea of failure is often the elephant in the room that no one wants to mention or consider leading to expensive fights that cannot be won and do even more damage. Acknowledging and accepting failure as an option is the big deal and is a fundamental part of how successful businesses operate – they like success but also know how to suffer failure successfully (read the blog).
Finally, two more quotes:
- Sun Tzu in The Art of War: ‘The true objective of war is peace’
- Gandhi: ‘The weak can never forgive. Forgiveness is the attribute of the strong.’
The best way to deliver successful projects and avoid unnecessary conflict is to be strong, be prepared to forgive and seek a peaceful outcome or to walk away for destructive fights.
[1] For more on the power of ‘win-win’ negotiating see: http://www.mosaicprojects.com.au/WhitePapers/WP1032_Win-Win_Negotiating.pdf
[2] The phrase Pyrrhic victory is named after Greek King Pyrrhus of Epirus, whose army suffered irreplaceable casualties in defeating the Romans at Heraclea in 280 BC and Asculum in 279 BC during the Pyrrhic War. “If we are victorious in one more battle with the Romans, we shall be utterly ruined.”
[3] The width of the line on the Minard map represents the number of soldiers remaining in the Grande Armée at key points in their advance (fawn) and retreat (black) to/from the Russian border. For more see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/French_invasion_of_Russia
[4] For more on ‘non-attachment’ and conflict management see: http://www.mosaicprojects.com.au/WhitePapers/WP1041_Managing_Conflict.pdf